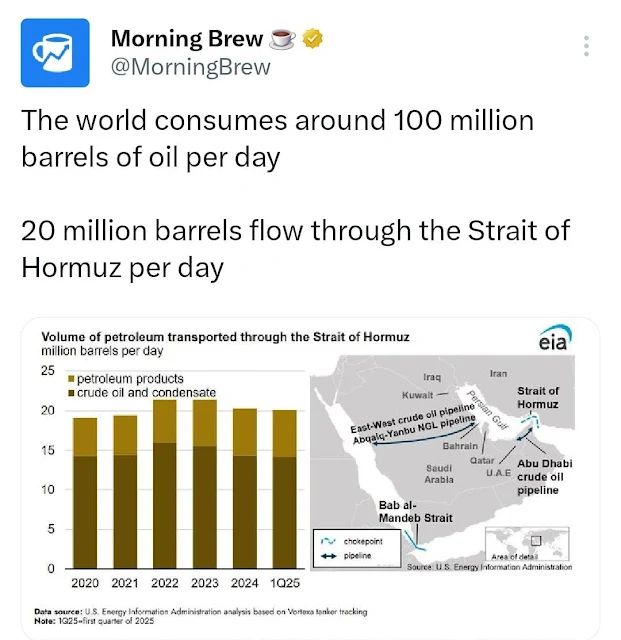
The Strait of Hormuz, a narrow sea passage between the Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea, holds unmatched importance in global oil trade. Every day, about 20 million barrels of crude oil—nearly 20% of the world's consumption—pass through this strategic corridor. In a world where over 100 million barrels of oil are consumed daily, the Strait’s significance cannot be overstated.
Let’s break down why this region is vital, and what the world risks if it gets blocked.
Global Oil Consumption vs. Hormuz Flow
According to recent global energy reports, the average daily oil demand worldwide is 100–104 million barrels per day (bpd). Of this, approximately 20 million bpd flows through the Strait of Hormuz. That means 1 in every 5 barrels consumed globally travels through this narrow channel—making it a critical lifeline for global energy markets.
Key Figures: Strait of Hormuz & Global Oil Flow
| Metric | Data |
|---|---|
| Global Daily Oil Consumption | ~100–104 million barrels (2025 est.) |
| Oil Passing Through Hormuz | ~20 million barrels per day |
| Width of Strait | 21 miles (only 2-mile shipping lanes) |
| Main Importers | India, China, Japan, South Korea, EU |
| Countries Bordering the Strait | Iran, UAE, Oman |
What Happens If Hormuz Is Blocked?
If the Strait of Hormuz is shut down due to conflict or geopolitical escalation, global oil supplies would immediately tighten. Oil prices could surge to $120–$150 per barrel, as seen in previous regional tensions.
Since alternatives like pipelines through Saudi Arabia and UAE can carry only a fraction of the total volume, global markets would face severe short-term disruptions.
India’s Stake in Hormuz
India, as the world’s third-largest oil importer, is directly impacted by developments in the Strait. A large portion of India’s crude imports from Iran, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia pass through Hormuz. Any instability could:
- Increase fuel prices in India.
- Disrupt supply chains.
- Affect inflation and the national budget.
Why This Strait Is a Flashpoint
Several reasons make the Strait of Hormuz a geopolitical hotspot:
- Iran’s Control: Iran borders the northern edge of the strait and has previously threatened closure in response to sanctions.
- Global Military Presence: The U.S., UK, and Gulf countries patrol this area to ensure free passage.
- Chokepoint Risk: Its narrow width and heavy traffic make it susceptible to blockades or targeted strikes.
Final Words
The Strait of Hormuz is not just a waterway—it's a critical artery for global oil movement. With over 20% of oil traded daily passing through it, any threat to its security has global ramifications. Whether you're in New York, New Delhi, or Nairobi, a disruption in Hormuz would be felt at your nearest petrol station.
As the world watches rising tensions in the Middle East, the future of this crucial corridor remains a vital focus for diplomats, economists, and energy experts alike.





0 Comments